What is NFC?
NFC (Near Field Communication), jointly developed by Philips and Sony, is a contactless identification and interconnection technology that enables close wireless communication between mobile devices, consumer electronics, PC, and smart control tools. NFC provides a simple, touch-based solution that allows consumers to exchange information, access content and services simply and intuitively.
NFC integrates contactless card reader, contactless card, and peer-to-peer functions into a single chip, creating countless new opportunities for consumers’ lifestyles. This is an open interface platform that can set up wireless networks quickly and actively. It is also a virtual connector for existing cellular networks, Bluetooth, and wireless 802.11 devices.
What is the Range of NFC?
Theoretically, the maximum NFC tag range is 20 cm. But, in the real world, you would rarely find a reader of that range. This makes sense because NFC technology should be used at a relatively close distance for security reasons.
At a shorter identification distance, NFC can diminish the probability of undesirable capture, especially to prevent our credit cards or bank cards from being remotely stolen by criminals. Mostly it requires you to tap the tag, which makes it more secure to pay with NFC.
NFC VS RFID:What is the difference?
Like RFID, NFC information is also transmitted by electromagnetic induction coupling in the wireless frequency part of the spectrum. But there is still a big difference between the two.
1、NFC is a wireless connection technology that provides easy, secure, and rapid communication. Its transmission range is smaller than that of RFID, and RFID can reach several meters or even dozens of meters. However, NFC adopts the unique signal attenuation technology and has some advantages that RFID does not have. For example, short distance, high bandwidth, low energy consumption, etc.
2、NFC is compatible with the existing contactless smart card technology and has become a formal standard supported by more and more major manufacturers.
3、NFC is also a short-range connection protocol that provides easy, secure, rapid, and automatic communication between various devices. Compared with other connection methods in the wireless world, NFC is a kind of close private communication.
4、RFID is more used in production, logistics, tracking, asset management, while NFC plays a huge role in access control, public transportation, mobile payment, and other fields.
NFC VS Infrared & Bluetooth
NFC is also superior to infrared and Bluetooth transmission. As a consumer-oriented trading mechanism, NFC is faster, more reliable, and much simpler than infrared, and does not require strict alignment to transmit data. Compared with Bluetooth, NFC is suitable for short-distance transactions and exchanging important data such as financial information or sensitive personal information.
Bluetooth can make up for the lack of NFC communication distance and is suitable for long-distance data communication. Therefore, NFC and Bluetooth complement each other and co-exist. The fast and lightweight NFC protocol can be used to guide the Bluetooth pairing process between two devices, promoting the use of Bluetooth.
Comparison between NFC, Bluetooth and Infrared
| Item | NFC | Bluetooth | Infrared |
| Network Type | Peer-to-Peer | Point-to-multipoint | Peer-to-Peer |
| Use Distance | ≤0.1m | ≤10m | ≤1m |
| Transmission Rate | 106, 212, 424 kbps, up to 868 kbps | 2.1 Mbps | ~1.0 Mbps |
| Response Time | < 0.1s | 6s | 0.5s |
| Security | High security (hardware implementation) | High security (Software implementation) | No security features (except when using IRFM) |
| Communication Mode | Active-active/passive | Active-Active | Active-Active |
| Cost | Low | Medium | Low |
How does NFC work?
NFC is a short-range high-frequency radio technology. The NFCIP-1 standard stipulates that the communication distance of NFC is within 10 cm, the operating frequency is 13.56MHz, and the transmission speed is 106Kbit/s, 212Kbit/s, or 424Kbit/s. The NFCIP-1 standard specifies the transmission speed, codec method, modulation scheme, and frame format of the RF interface of NFC equipment in detail. It also defines the transmission protocol of NFC, including startup protocol and data exchange method.
NFC communication technology evolved from contactless RFID and is backward compatible with RFID, which is mainly used to provide M2M (Machine to Machine) communication in handheld devices such as mobile phones. There are three main working modes of NFC terminals:
1、NFC Active Mode
Because both the originating device and the target device must actively generate RF fields when sending data to each other, so this mode is called active mode. They both need power supply devices to provide the energy to generate RF fields and can take turns transmitting signals to each other.
The NFC terminal can act as a card reader and emit RF fields to identify and read/write other NFC device information. This mode of communication is the standard model for peer-to-peer communication and can achieve very fast connection rates.
2、NFC Passive Mode
In NFC passive mode, the NFC originating device (also known as the primary device) needs a power supply device. The master device uses the power supply device to provide the RF field and sends the data to the NFC target device (also known as the slave device).
The RF field generated by the primary device is used to power the circuit of the slave device. Data sent by the primary device is received. Load modulation is used to transmit data from the slave device back to the primary device at the same speed.
Because this working mode does not generate the RF field from the device, but passively receives the RF field generated by the master device, it is called passive mode. In this mode, the NFC master device can detect a non-contact card or NFC target device and establish a connection with it.
3、Bidirectional Mode
In this mode, both NFC devices are in the active mode that they can actively emit RF fields to establish peer-to-peer communication. NFC-enable devices can exchange data in active or passive mode.
In passive mode, the device that initiates NFC communication, also known as the NFC sponsor, provides the RF field throughout the communication process.
At present, our common NFC working mode is the passive mode, very suitable for swiping the mobile phone to take the bus, shopping, etc. Active mode is commonly seen in reading NFC tag information. And the bidirectional mode is mostly used for information exchange, such as exchanging business cards.
NFC Functional Mode
1、Read/Write
In this mode, phones with NFC enabled can read and write any NFC tags and obtain the data from it.
2、Peer-to-Peer
Two NFC devices can exchange data. For example, you can share a Bluetooth or Wi-Fi password to start Bluetooth or connect to Wi-Fi. You can also exchange data such as virtual business cards or digital photos.
3、Card Emulation
NFC-enabled phones act as readers when interacting with tags. In this mode, the mobile phone can also be used as a tag or a wireless card to be read.
NFC Standard
ISO 14443
ISO 14443 is a well-known international standard originally designed for contactless chip cards in 13.56MHz radio communications. ISO 14443 defines a protocol stack from the wireless layer to the command protocol. There are two versions of wireless layer ISO14443-2, which have different modulation and bit coding methods.
ISO 14443 specifies two versions of the package framework and the underlying protocol portion (ISO 14443-3). The highest layer of the ISO stack defines the command interface (ISO 14443-4) that transmits information.
NFCIP-1
NFCIP-1 protocol is based on ISO 14443. The main difference is a new command protocol that replaces the top layer of the previous protocol stack. NFCIP-1 includes two communication modules that enable NFC devices to operate in peer-to-peer mode and also support communication with NFCIP-1-based NFC tags.
MIFARE
MIFARE refers to the type of NFC tag developed by NXP Semiconductor. MIFARE tags are widely used in memory cards for transport applications. ISO 14443 defines the protocol stack from the wireless layer to the command protocol.
FeliCa
FeliCa is a patented NFC tag technology developed by Sony, which is widely used in exclusive payment and transportation applications in Asia. FeliCa tags are also integrated into the mobile phone model of the mobile FeliCa system. Felica tags belong to the Japanese industry standard. The tag is based on ISO 18902 in passive mode, with additional authentication and encryption features.
NFC Forum Type
Type 1
- Type 1 tags are cheap and suitable for a variety of NFC applications
- Based on ISO-14443A standard
- Readable and rewritable and configurable as read-only
- 96-byte memory, scalable to 2KB
- Transmission rate 106kbits/s
- No data conflict protection
- Compatible products: Innovision Topaz, Broadcom BCM20203
Type 2
- Type 2, like type 1, is derived from the NXP MIFARE Ultralight tag
- Based on ISO-14443A standard
- Readable and rewritable and configurable as read-only
- 96-byte memory, scalable to 2KB
- Transmission rate 106kbits/s
- Support for data conflict protection
- Compatible products: NXP MIFARE Ultralight
Type 3
- Type 3 is derived from the unclassified part of the Sony FeliCa tag. It is more expensive than the label of type 1 and 2, suitable for more complex applications
- Based on the Japanese industry-standard (JIS) X 6319-4
- Define properties that are readable, rewritable, or read-only at production time
- Variable memory, up to 1MB space
- Two transfer rates are supported: 212 or 424kbits/s
- Support for data conflict protection
- Compatible products: Sony FeliCa
Type 4
- Type 4 is similar to type 1 in that it is derived from the NXP DESFire tag
- Based on ISO-14443A standard
- Define properties that are readable, rewritable, or read-only at production time
- Variable memory, up to 32kB
- Three transfer rates are supported: 106,212 or 424kbits/s
- Support for data conflict protection
- Compatible products: NXP DESFire, SmartMX-JCOP
Type 5
- It is the latest type of NFC tag defined in recent years. NFC Forum introduced this series of chips to meet the growing variety of long-distance, miniaturized NFC tags, and their applications
- Based on ISO-15693 standard
- Readable and rewritable
- Variable memory: 256 bits, 896 bits, 1280 bits, 2528 bits
- Up to 53kbits/s
- Support for data conflict protection
- Compatible products: ICODE SLI-Xseries/TI 2K/ST LRI2K
Type 6
- This type is only compatible with some mobile phones
- Based on ISO-14443A standard
- Readable and rewritable
- Variable memory: 1KB,4KB
- Data transfer of 106kbits/s
- Support for data conflict protection
- Compatible products: M1(S50,F08)
NFC Application
NFC mobile phone has a built-in NFC chip, a part of the RFID module, which can be used as an RFID passive tag-to pay for fees, or as an RFID reader-for data exchange and acquisition. NFC technology supports a variety of applications, which can be divided into the following five categories:

Touch and Go: Such as access control management, tickets, logistics management, and so on. All that users need to do is put the NFC tag close to the card reader. Common NFC products for such applications include the NFC keychain, NFC card, NFC wristband.
Touch and Pay: Such as contactless mobile payment. The user can make payment and confirm the transaction by placing the device near the POS terminal embedded with NFC module.
Touch and Connect: Connect two NFC devices for peer-to-peer data transmission, such as downloading music, sending pictures to each other, exchanging address books, etc.
Touch and Explore: Users can browse the relevant information by putting the NFC phone close to the smart public phone or poster with NFC function on the street.
Load and Touch: Users can receive and download information through the GPRS network for functions such as payment or access control. For example, users can send text messages in a specific format to the mobile phone of the housekeeper to control the housekeeper’s access to the house.
Common NFC Tags

NFC Stickers
NFC stickers are a low-cost NFC solution that almost all of us can afford. There is a small NFC chip in it and usually encapsulated by paper, PVC or PET material. NFC stickers come in many chips, sizes, colors, patterns that you can choose according to the applications. Common NFC Chips are Ntag213/ 215/216, DESFire EV1, M1, Topaz 512, etc. NFC stickers are widely used in advertising, consumer electronics, gaming, healthcare, retail, social media, and other fields.
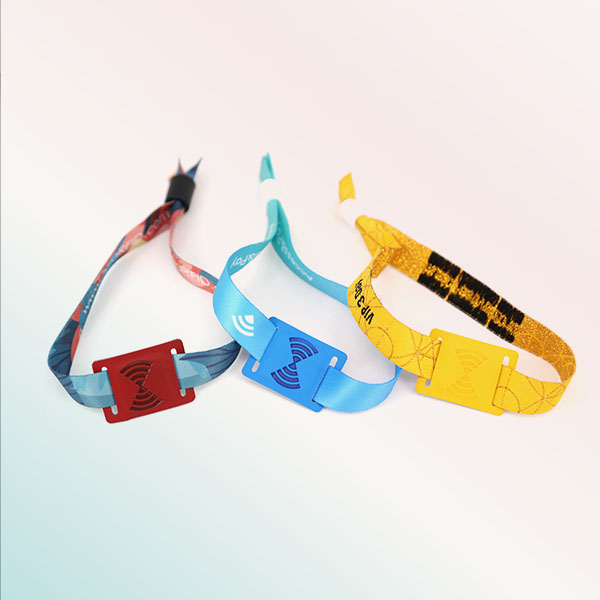

NFC Wristband
NFC wristband, another packaging form of NFC tags, combines fashion and intelligence. In addition to a variety of chip options, wristband styles are varied and colorful, common are silicone wristband, fabric wristband, PVC wristband, paper wristband, etc. NFC wristband can be customized, choose your brand color, printed with your LOGO, is an excellent marketing method. It is often used in festivals, events, medical management, playgrounds, gyms, etc.

NFC Card
NFC card is the most common form of NFC packaging. The standard size is CR80. NFC card has high-security performance and is often used in applications that require high-security performance. Our subway card, bus card, shopping card, and membership cards are NFC cards. Besides, the game card used by people who like to play Amiibos is also an NFC card.NFC cards have white cards and printing cards according to customer requirements.

NFC Anti-metal Tag
NFC anti-metal tags are specially designed to work well on metal surfaces. One side is paper, PVC, PET, or other material, and the other side is an anti-metal sticker. The common sizes are 20mm diameter, 25mm diameter, 35mm diameter, etc. It is a perfect NFC solution for some special applications that need to work on the metal surface. For example, IT asset management, medical device management, consumer electronics, etc.
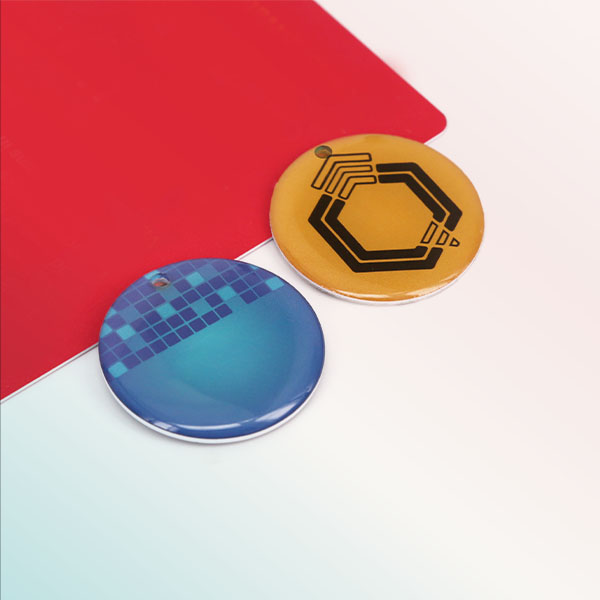
NFC Epoxy Tag
This NFC tag has an attractive appearance like a crystal clear button, small and exquisite. It is made of epoxy material and has the characteristics of corrosion-resistant, anticollision, waterproof, and durable. You can define what it like, circle, square, heart shape, or animal shape as well as pattern inside it. It is very suitable for access control management, pet management, parking management, child pickup, cashless payment, social interaction, etc.
Q & A
Well, if your phone has the NFC function, you can do many interesting things to make your life convenient and smart. For example, you can share contacts, websites, videos, or images with your friends. You can pay directly with it without worrying about forgetting your metro card or bank card. With NFC tags, you can control your lights, your washing machine, or set an alarm clock to get you out of bed. Want to know more, you can click here.
It depends on how often you use the NFC feature. If you use it frequently, you don’t have to turn it off, which is more convenient. If you use less, it’s better to turn it off. As we all know, smartphones consume more power, and turning it off can save the battery of the phone.
NFC, short for Near Field Communication, is a new technology that allows users to achieve more functions, such as NFC payment, exchanging digital content, connecting electronic devices with a touch. Nowadays, in addition to Samsung phones, many Android phones have NFC function.
Turning on the NFC function has an impact on the battery life of the mobile phone, but negligible. Nowadays, smartphones almost need to be recharged every day because of their multi-functions. But if you don’t use it often, it’s better to turn it off.
This is a misunderstanding of the function of NFC. NFC can exchange data and must be close to each other. And it cannot be used to monitor and allow the theft of other people’s information and data.
NFC technology is secure, and it has many chips to choose from, some of which have a high encryption level and good security performance. Besides, it uses the signal weakening decline technology, which only allows short-distance recognition, and its security performance is better than that of RFID. Many consumption cards, transportation cards, and bank cards also use NFC technology.
Relevant articles
- 26 Ingenious Ways You Can Do With NFC Tag Uses
- NFC vs. RFID: What’s the Difference Between Them?
- Common RFID Standards and Protocols You Must Know
- NFC vs. RFID: What’s the Difference Between Them?
- Learn The Truth About RFID Sticker Structure And Material
- What is RFID tag? Learn about common RFID applications






