
NFC and Bluetooth are the two most common data sharing techniques. While both of them promote wireless communication, several differences exist.
So, what’s the difference between NFC and Bluetooth?
Bluetooth is the older of the two technologies. It was developed by Nils Rydbeck in 1989, becoming the pioneer of wireless data technology. The technique allows users to share data between nearby Bluetooth-enabled devices.
On the other hand, NFC is a recent wireless data communication technology. It uses radio waves to pass data from one device to the other. However, it has a shorter transmission distance than Bluetooth.
This article gives a detailed analysis of the two communication technologies. By the end of the article, you’ll have in-depth knowledge of their similarities and differences. Read on.
NFC – What Is It?
Near Field Communication (NFC) is a wireless technology that allows the exchange of data between NFC-enabled devices. The communication technique is short-range and requires that the two devices are in close proximity.
How NFC Works
NFC allows device owners to send and receive information using radio waves. The technology uses the Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) concept.
When two compatible devices come in close range, they detect the NFC-induced electromagnetic field and pair. After pairing, the devices will exchange data without requiring any other external powering.
The transmission frequency used for NFC data transfer is 13.56 MHz. You can send data at 106-424 kilobits per second, which is ideal for quick swapping of files.
NFC Modes of Operation
NFC has 3 modes of operations, including:
- Peer-to-Peer Mode. This is the mode that applies when sending and receiving data between smartphones. The two devices will switch between active (when sending data) and passive (when receiving data).
- Read/Write Mode. This mode only allows for one-way data transmission. As such, the active device (most likely your smartphone) will link with a device that captures the information in it.
- Card Emulation Mode. This mode enables you to use your smart card and other contactless payment cards for your payment.
In all these modes, there must be two devices – one passive and the other one active. The active device will send the data while the passive one will receive.
In cases of card emulation, the passive device is called the interrogator. It reads and analyzes the data for authentication before approving any transaction.
NFC Applications
Due to the NFC’s efficacy, various industries have adopted its use. Some of the key applications for NFC include:
- Online Payments. NFC is a popular technology used when making smart cards and other contactless payment methods. Its short read range guarantees security for the cardholders.
- Access Control. Many organizations use NFC technology to validate visitors’ identities before allowing them to access high-security zones.
- Asset Tracking. NFC tags are essential in storing crucial information about assets. You can store information such as the maintenance schedule, serial number, asset value, and purchase date. The ease to retrieve and monitor the data makes inventory management a breeze.
- Wireless Pairing. NFC technology allows the automatic pairing of two compatible devices within the acceptable read range (usually a few centimeters). This technique makes it easy for you to share and receive data.

Bluetooth
Just like NFC technology, Bluetooth is a wireless technology ideal for data exchange between two enabled devices. It uses UHF radio waves with frequencies ranging from 2.402 to 2.480 GHz.
However, this technology requires a manual pairing of the two devices before the data transmission process can start.
It divides the data into packets before transmitting them on one of the 79 designated Bluetooth channels. Each of the channels has a bandwidth of 1 MHz, allowing the transfer of lots of data within a short time.
How Bluetooth Works
If you want to share data with another device, you must be close enough to it. Once close, you should activate Bluetooth on your device. When active, your device will detect other enabled devices within the acceptable range.
The connection uses a concept called the spread-spectrum frequency hopping. In this technology, the two pairing devices will pick a connection channel from the 79 available ones. If the channel is already engaged, it will randomly shift to the other available channel.
After connecting, you’ll easily send or receive data from the paired device. Interestingly, you can pair up to 8 devices at any given time.
When this happens, all the 8 devices will form a mini-computer system called the piconet. Any device can join or enter the piconet at any given time. The whole system will be under one device called the Master.
For guaranteed security, the Bluetooth data exchange system has mechanisms to reduce interference from other electrical devices. For example, pairs of devices will regularly shift the frequency thousands of times per second. This creates unpredictability and makes it pretty hard for anyone to interfere with the data transfer process.
NFC vs. Blue Tooth- A Detailed Comparison
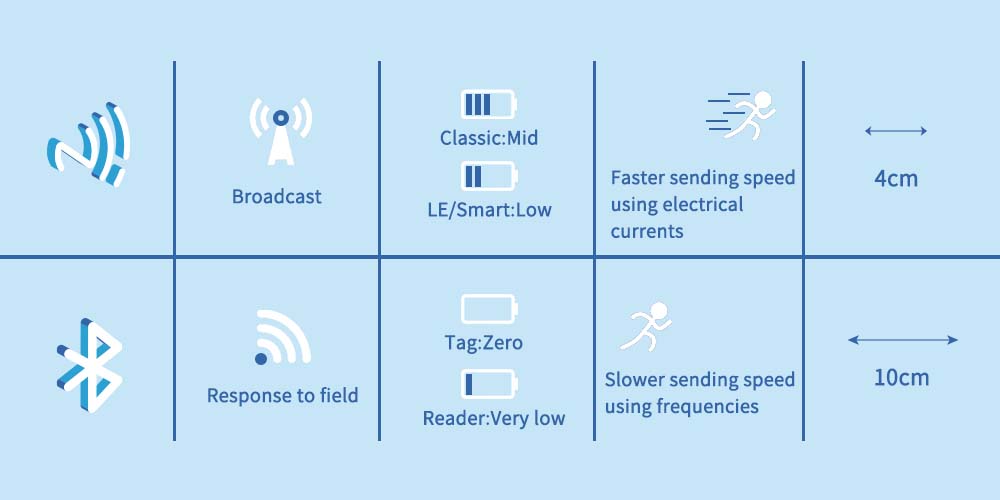
While both NFC and Bluetooth use wireless technology to exchange data, several differences set them apart. Here are the key differences between the two communication techniques:
- Connection Capacity. One NFC-enabled device can only connect to one other device. On the contrary, Bluetooth allows the connection of up to 8 devices at any given time.
- Technology. NFC uses electromagnetic radio fields to connect two devices, while Bluetooth uses direct radio transmissions.
- Frequency Wavelength Used. NFC uses 13.56 MHz communication frequency while Bluetooth uses approximately 2.04 GHz frequency to transfer data
- Read Range. Using NFC allows you to transfer data within a range of 4 cm. When using Bluetooth, you will transfer data within a range of approximately 10 cm.
- Data Transfer Rate. The maximum data transfer rate for NFC is 424 kbits/sec, while that of Bluetooth is 1-3 Mbit/s. As such, the data transfer process is faster when using Bluetooth.
- Power Consumption. When using NFC for data transfer, you will consume lesser power than when using Bluetooth
NFC vs. Bluetooth: Which Is Better?
NFC is an economical, wireless data transfer system since you’ll require less energy to send and receive data. However, the power efficiency comes along with a few drawbacks.
For example, NFC has a shorter transmission range than Bluetooth. Additionally, NFC is slower in data transmission. As such using the technology requires more data transfer time than when using Bluetooth.
However, NFC offers faster connectivity. As long as you have an NFC-enabled device within the acceptable read range, then the connection will happen automatically through inductive coupling. Due to the lack of manual pairing requirement, the NFC technology becomes convenient when using contactless payments.
It is due to this fast connectivity that many smartphone manufacturers have integrated NFC in their devices. This makes tap-and-pay options available for its users.
Now that we’ve looked at all the elements of NFC and Bluetooth, it’s time for the verdict! So, which is the better technology between the two?
Well, the technology you choose will largely depend on your needs. If you need to transfer a large volume of files to many devices, then Bluetooth will come in handy. On the other hand, NFC is the best technology if you’re a fan of contactless payment.
When is NFC better than Bluetooth?
NFC is better than Bluetooth under the following circumstances:
- When You Need Fast Pairing. Unlike Bluetooth, NFC does not require manual pairing, making file transfer fast and convenient
- When You Want to Use Contactless Payments, NFC is the better option for completing mobile payments. It offers a safe and efficient payment platform.
- When You Value Anonymity, unlike Bluetooth, you can use NFC without leaving behind any records after completing the process of data transfer.
What Are the Similarities between NFC and Bluetooth?
Both NFC and Bluetooth are wireless technologies that allow users to transfer data within a short distance.
Compared to other sharing methods, the techniques guarantee a fast and efficient data transfer channel.
However, both the sender and the recipient need to have NFC or Bluetooth-enabled smartphones to complete the data exchange process.
Is NFC Safer than Bluetooth?
NFC is generally safer than Bluetooth. The enhanced security is attributed to its short transmission distance.
Unlike Bluetooth, you must be around 4 cm away from the other device for data transfer to occur. As such, there are zero chances that anyone can read your NFC-device from afar.
Due to this security feature, NFC is the preferred technique for contactless payments. It guarantees that the transaction will only occur with the consent of the device owner.
Conclusion
NFC and Bluetooth are platforms that can serve you right depending on your interests. Bluetooth is your ideal choice if you want an effective data transfer method. It is faster than NFC and allows you to pair up to 8 devices at any given time.
If you’re looking for a safe contactless payment option, then you should consider an NFC-driven technique. NFC has a shorter read range, which guarantees security. Additionally, the technology does not require manual pairing, thus guaranteeing fast and convenient transactions.
Whichever technique you choose, just ensure that it serves you right. That way, you will enjoy optimum data transfer and payment options.






