You may have applied RFID in the course of your daily business activities, but how conversant are you with the advancement of the technology? Just like any other technology in an application, innovations are inevitable. The major revolution in the RFID world is towards reducing the size of RFID tags.
Radio Frequency Identification tags, Abbreviated as RFID, are micro-devices that rely on low-power radio waves for the reception, storage, and transmission of data to nearby readers. RFID tags are made of three crucial parts: an integrated circuit or a microchip, a layer of protective material holding the components together, and an antenna.
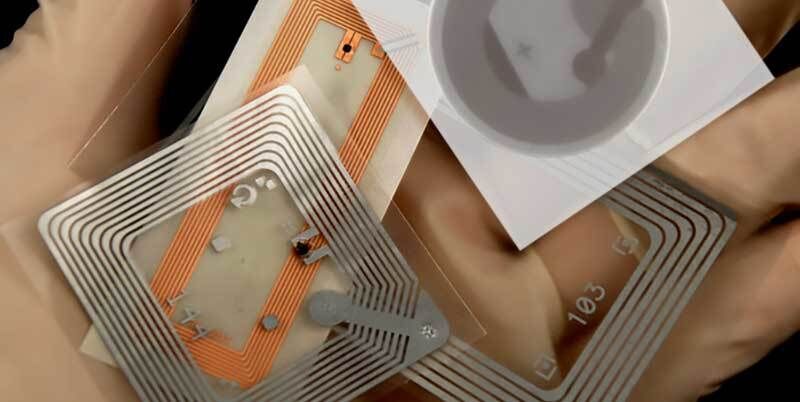
The three major types of RFID tags in the market: passive, battery-assisted passive (BAP) or the semi-passive, and the active RFIDs. Passive RFID tags use electromagnetic power that is transmitted from an RFID reader because the tag itself does not have an internal power battery. On the other hand, active RFID tags have their power source and transmitter on-board the tag. The battery-assisted passive or basically the semi-passive tags are a modification of the passive tag by incorporation of a power source.
Radio Frequency Identification tags operate in multiple frequency ranges: high frequency (HF), low frequency (LF), and the ultra-high frequency (UHF).
An RFID tag can be fixed on different surfaces, and the tags are available in a variety of designs and sizes. The tags come with an array of form factors ranging from labels, hard tags, dry inlays, wet inlays, fobs, cards, and stickers.
How small can an RFID tag be?
The chip size is one of the challenges that has been facing the RFID technology. Although developers are trying to make the chips as small as the size of a rice grain, that size is still huge for some applications. Developers are working towards making the chips as small as possible.
Researchers are the University of Stanford running a project of developing a 60GHZ passive RFID tag that is as small as to fit in a human body cell. The team of developers has managed to scale down the size of the antenna and the chip to 22 microns (that is about 0.0009 inches) wide. This is the size of a fifth of the diameter of human hair and is small enough to fit in a human cell.
If this project becomes a success, the RFID tag will be used to read throughout the human body. This chip has already been inserted into a melanoma cell of a mouse. It can also be inserted into a larger mass of cells like the case in a tumor.
The researchers have further developed a customized RFID reader that will transmit data and receive responses from the micro-tag. According to the researchers, this micro RFID tag and the specialized reader are a promising move towards real-time continuous monitoring activities at the basic cellular level.
Both Murata and Hitachi are developers of very small RFID tags. While the smallest Murata tag measures about 700 microns (0.03 inches), the smallest Hitachi tag measures approximately 300 microns (0.01 inches).
The RFID tag developed by the Stanford University team is too small to be seen by the naked eye. The team is calling the tag a Micrometer-Scale Magnetic Resonance-Coupled RFID Transmitter for Wireless Sensors in the Cell. The goal of the project is to create an RF enhanced antenna at the microscopic level, to be used for research and health diagnostic purposes.
Application of Small RFID Tags
Below are some of the applications or uses of small RFID tags:

1. Human Implantation
The Biocompatible Microchip Implants that are implanted into the human body rely on RFID technology. This field relies on the miniaturization of the RFID tags as the microchips implanted into the body are as small as 22 microns.
The use of RFID chips in humans was approved in the United States by the Foods and Drug Administration in 2004.
However, there is a lot of controversy surrounding the implantation of RFIDs in humans as advocates of privacy claim that hackers can scan and manipulate the information stored in the microchips.
2. Medical equipment
The healthcare industry demands an increase in efficiency, visibility, and sourcing of data from the relevant interactions. The industry borrows heavily from RFID tracking to help in facilitation and enhancement of the management of medical equipment, monitoring environmental conditions such as temperature, improving patient workflow, and protection of patients and staff from hazards such as infections.
The adoption of RFID technology has proved to be very effective. Hospitals majorly employ active RFID to track high-value assets and passive RFID in tracking low-cost items at the room level.
3. Libraries
Libraries across the world are replacing the use of barcodes with RFID on books. The RFID tag can be a key to the library’s database, or it might as well hold information about a particular book or item. Apart from helping with tracking of the books, these tags come in handy in self-service checkout and inventory management. They also double as a security device replacing the traditional electromagnetic security strip.
4. Commerce
Businesses are using RFIDs to identify, organize, and manage stock, equipment, tools, among other assets, without necessarily having to make entries manually. Final consumer products such as wearables and automobiles can be tracked from the factory and through the shipment process to the final consumer. Many people have employed automatic RFID identification to manage their inventory systems.
As a common practice, manufacturers require their vendors to use RFID tags on all products so as to effectively and easily manage the supply chain.
5. Advertising
Facebook issues RFID cards at their live events. This card allows the guests to capture and post pictures automatically.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Small RFID Tags
The RFID technology has greatly advanced and is more common in logistics and supply chains. The use of RFID tags enhances accurate and fast inventory tracking as well as allowing enhanced security features. Due to the miniaturization of the RFID tech, RFID tag size has greatly reduced as developers produce micro tags. Today, there tags small enough to fit into animal and human cells.
The use of small RFID tags has a myriad of advantages. Some of the advantages associated with the miniaturization of the RFID technology include the following:
1. Identification Is Permanently Stored
This is one of the key advantages of having an implantable RFID tag as it creates permanent identification. Once the data has been encoded into the RFID tag, it cannot be stolen or lost. One can only read the encoded information using a close-range scan within the location of the tag. With RFID technology, mixups in places such as hospitals are prevented, and it becomes easier to identify missing persons.
2.Pet Microchipping
The advancements in this technology have seen the development of implantable small RFID tags, although they are yet to gain popularity in the human application, they come in handy in pet identification. Pet Microchipping involves the implantation of a small tag into the pet that will allow veterinarians to scan animals that have displaced their identification tags.
Handlers can easily identify a lost animal by scanning the RFID microchip. This tag also stores information on the special needs of the animal, such as medication and feeding habits.
Although it has its advantages, the use of Radio Frequency Identification has its downside as well. Some of the disadvantages of using RFIDs include:
- Privacy concerns
The growth of RFID has posed potential privacy concerns on technology. This problem is majorly associated with the use of small RFID tags. To use it with its corresponding database, a small RFID tag contains a unique identification number. The threat comes in when a third-party scanner accesses this identifying number allowing third-parties to use it for tracking your assets.
Anyone with a strong RFID scanner and close enough to your tag can read it. Without the reliance on a corresponding database, it would not be impossible for third party scanners to read your tag. However, this does not mean your privacy is secured since one can monitor your movement using a unique identifier.
- Health Concern
Just like any other foreign object in your body, RFIDs implanted in the body could cause health complications. You might not experience trauma due to the extremely small size of the chips, but the downside to this is that the injection area might get infected. Over time, the implanted microchips may end up on the surface of the skin, causing skin complications.
Again, if a highly strong RFID pulse is used, the chips might get damaged, causing trauma and irritation to the surrounding body tissues.
Miniaturization of RFID is the ongoing revolution in the industry. Developers have focused on reducing the size of the chips into ultra-microchips. The reason for this approach is increasing the application of RFID is areas such as the medical field where RFID chips are implanted into the human cells. The only way to achieve this objective is by reducing the size of RFID tags.







where can rfid chips be placed? in the case of a manufacturing plant?
Track and manage products, manage fixed assets, inventory management, etc.